Home / Medical Coding vs Medical Billing
Understanding the difference between medical coding and medical billing is important for those who are involved in healthcare revenue cycle management. These two interconnected processes form the backbone of accurate reimbursement, ensuring that healthcare services are documented correctly, claims remain compliant, and payments are received on time.
When you see medical coding and medical billing that are often written together, they look familiar, but each plays an important role in the revenue cycle. When coding inaccuracies, claim denials, delayed reimbursements, or compliance risks occur, the impact is felt directly in cash flow, operational efficiency, and administrative workload.
Medical coding is the process of converting clinical records into universal alphanumeric codes recognized by payers, regulators, and health organizations in the form of ICD-10, ICD-11, CPT and HCPCS. It is the first step in medical billing and medical coding. Medical coding is used for documentation and claim submission.
Coders use standardized systems such as:
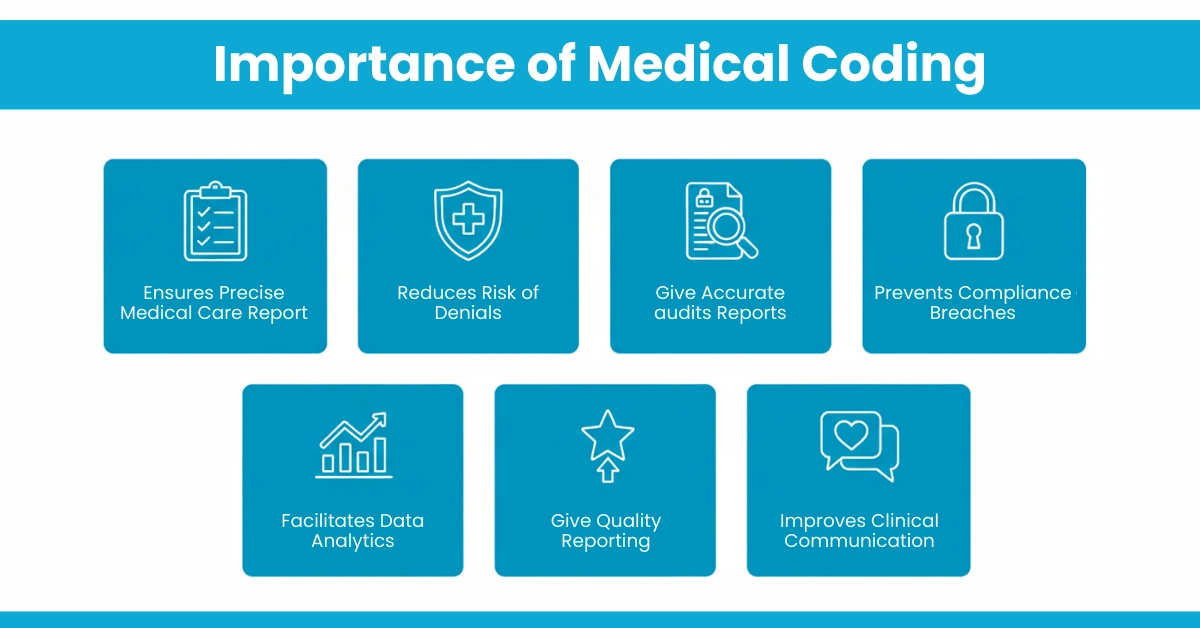
Importance of Medical Coding:
For example, if a patient visits for uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes, the coder would assign ICD-10 code E11.65. If the provider performed a comprehensive office visit for an established patient, the coder might assign CPT code 99215.t
Medical billing uses standardized codes to prepare, submit, and manage claims with insurance companies and patients. It transforms clinical services into actual revenue.
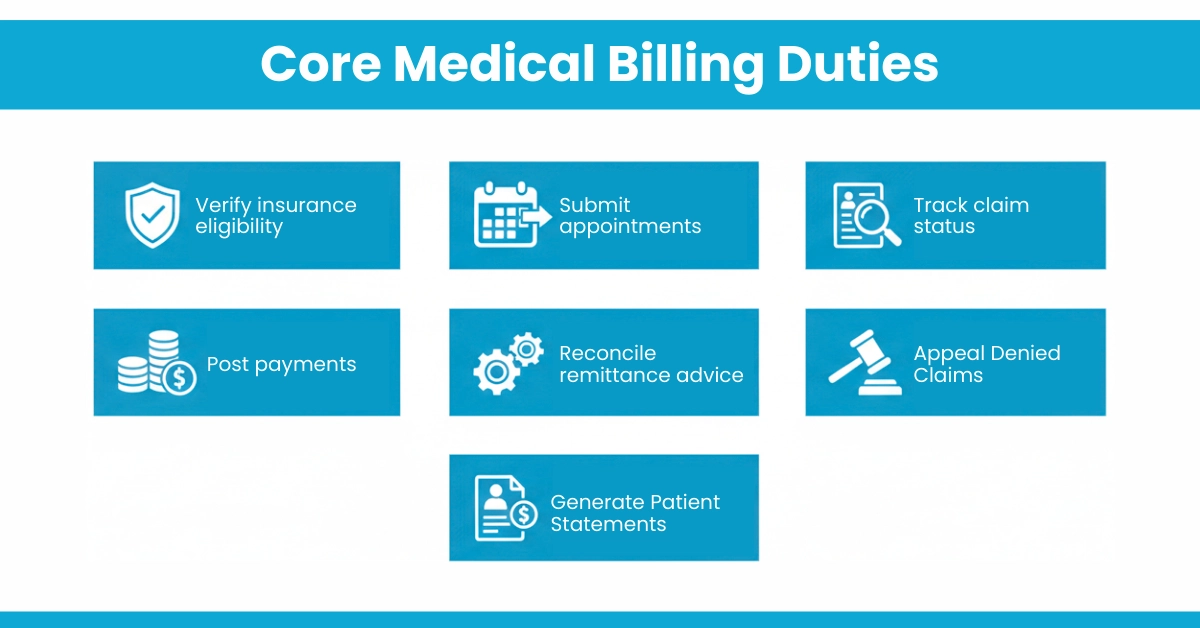
What do medical billers do? After medical coders assign the appropriate codes, billers create and submit claims to insurance companies just like our in-house team do. They verify patient insurance eligibility, calculate patient responsibility, post payments, manage denials, and handle patient billing inquiries. Their primary goal is to ensure timely and accurate reimbursement for healthcare services.
Core Medical Billing Duties
Hello MDs supports these tasks through our payment posting and denial management services, making sure reimbursements come in faster and with fewer headaches.
The table below highlights the fundamental distinctions between these two critical functions.
Aspect | Medical Coding | Medical Billing |
Core Focus | Translating clinical care into universal data codes. | Translating coded data into financial claims and securing payment. |
Primary Input | Physician’s notes, operative reports, lab findings. | Encounter form with diagnoses and procedure codes from the coder. |
Key Tools/Systems | ICD-10-CM, CPT, HCPCS code books; encoder software. | Practice Management (PM) software, payer portals, and clearinghouses. |
End Product | Accurate, coded patient encounter record. | Clean claim submitted to payer; patient statement. |
Critical Skill | Analytical thinking, knowledge of medical terminology and coding guidelines. | Knowledge of insurance rules, payer contracts, and regulations; communication. |
Main Risk of Error | Incorrect reimbursement, compliance issues (fraud/waste/abuse). | Claim denials, delayed payments, and patient billing errors. |
Did you know?
According to AAPC, practices with certified coders experience up to 25% fewer claim denials compared to those without certified coding staff. This directly impacts how quickly billers can secure reimbursements and maintain healthy cash flow.
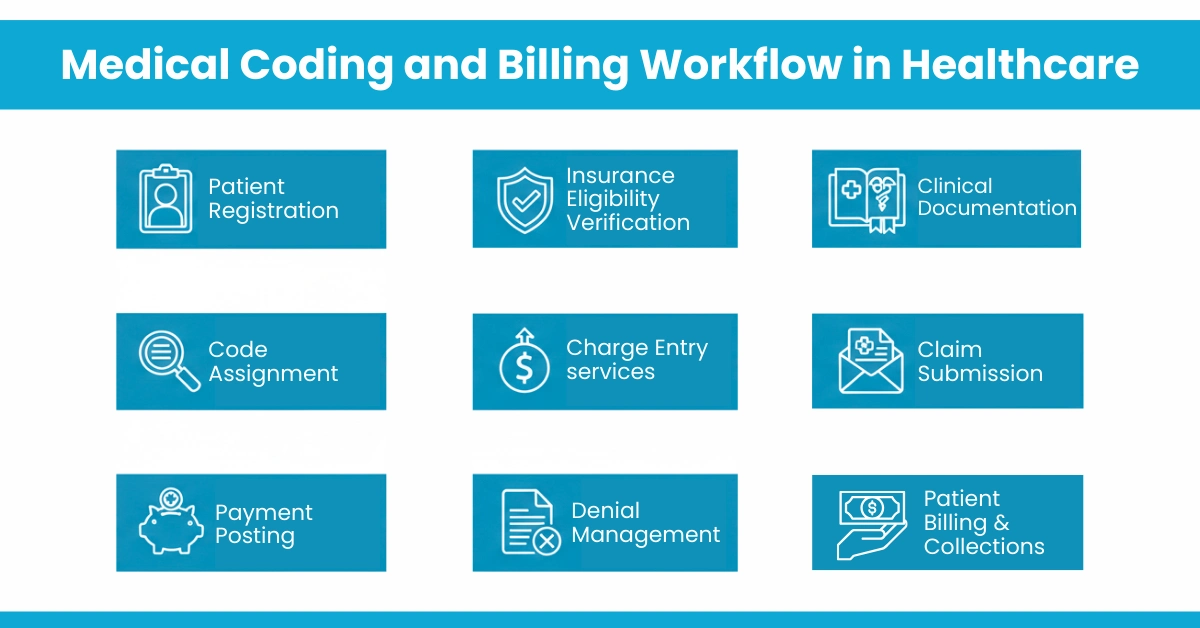
The journey from patient encounter to bank deposit reveals why coding and billing medical teams must operate in lockstep:
Modern practices verify benefits 48 hours before appointments. This insurance eligibility verification prevents downstream denials for non-covered services.
Providers document services clearly and completely. Poor documentation leads to coding errors
Coders review documentation and assign ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes. They must understand medical necessity requirements and query physicians for clarification when documentation is insufficient.
Coded services are entered accurately with correct modifiers and units
Claims are reviewed for errors and submitted to payers
Payments and adjustments are applied correctly to patient accounts.
When claims are denied, denial management specialists analyze root causes (coding errors, eligibility issues, medical necessity failures) and file appeals within tight payer deadlines.
Patient receives clear statements for remaining balances
Where errors happen: The most common breakdown points include incomplete documentation (impacting coding accuracy), incorrect code selection, eligibility verification failures, and insufficient denial follow-up. Each error point creates a ripple effect that delays reimbursement and increases administrative burden.
Tip for you: Practices using integrated RCM healthcare services report 15-20% faster collections compared to siloed billing departments. At HelloMDs, our charge entry services and accounts receivable management help close these gaps effectively.
Medical Coders
Medical Billers
Medical billing and coding duties now require cross-functional knowledge. A coder who understands payer reimbursement rules produces more valuable work, while a biller who recognizes coding patterns spots denial trends faster.
Both are indispensable. Here’s how they impact finances:
Common revenue challenges include:
Hello MDs addresses these points by combining AAPC-certified coding expertise and modern billing solutions to reduce denials, ensure correct claims, and enhance overall revenue performance.
Coding and billing are not isolated tasks; they are interdependent stages in a linear workflow that fuels your practice’s revenue cycle.
A breakdown at any point disrupts the entire flow. For example, if a coder uses an incorrect CPT code, the biller will submit an invalid claim, guaranteeing a denial. Similarly, if a biller misses a filing deadline, accurate coding becomes irrelevant, as the claim will be rejected.
For a complete picture of the billing side of healthcare, check out How Many Types of Medical Billing?. It pairs perfectly with our coding vs billing discussion, highlighting how correct coding ensures smooth billing and faster payments
Medical coding and medical billing are two different yet interdependent components of healthcare revenue cycle management. Accurate coding ensures clinical services are properly documented, compliant, and reimbursable, while effective billing ensures those coded services are converted into timely payments. Any breakdown in either process can result in denials, delayed reimbursements, and lost revenue. When coding and billing teams work in alignment, practices experience smoother cash flow, reduced compliance risk, and improved financial performance. By leveraging expert-driven medical coding and billing services, healthcare organizations can strengthen their RCM processes and focus more on delivering quality patient care.
Disclaimer:
This content is for general information only. Rules and guidelines may change, so always check with a qualified professional for accurate guidance. Some images used are AI-created and meant only for visual explanation purposes.
Accurate coding and billing reduce errors, unnecessary charges, and claim denials, helping control patient out-of-pocket costs.
Coding systems update annually to reflect new healthcare practices, procedures, and regulations, requiring regular training.
Errors like wrong codes, missing modifiers, unbundling, and incomplete documentation frequently cause claim denials.
Yes, inaccurate codes can mis-record medical history, potentially affecting future care and insurance coverage.