Home / Global Period in Medical Billing
When surgical procedures are bundled into a single payment, understanding the global period in medical billing becomes important for accurate reimbursement. Many practices lose thousands of dollars each year due to billing errors related to services that are incorrectly included and excluded from the global surgical package.
The CMS is implementing important changes in 2025-2026, including stricter audit procedures and new reporting requirements with HCPCS code G0559. Staying compliant has never been more important.
A global period in medical billing represents CMS’s bundled payment approach for surgical care. Instead of paying separately for each pre-op visit, the surgery itself, and every post-op checkup, Medicare and most commercial payers combine these into one comprehensive payment.
The global period definition includes three distinct phases:
Pre-operative period
Intra-operative period
Post-operative period
Insurance companies won’t reimburse separately for standard follow-up visits or typical post-operative care within this window. Instead, the surgical global period payment covers the surgeon’s work before, during, and after the procedure as a single bundled service.
The global period plays an important role in maintaining financial stability for healthcare providers. It ensures that the purpose of the global period is to bundle costs and encourage comprehensive care. It reduces the risk of overbilling and audits.
For Medical billers, strict adherence to CMS and Medicare Global period rules directly impacts reimbursement outcomes. Incorrect billing during the global periods can result in claim denials, delayed payments, or audits.
For providers and billers, the global period ensures:
Partnering with experts like HelloMDs helps practices navigate these rules efficiently, ensuring timely payments while reducing errors in E/M coding and surgical claims.
Understanding the types of global periods is fundamental to correct billing. Here’s the breakdown that every certified coder studies:
Follow-ups are billable separately. Ideal for minor procedures like biopsies
According to American Academy of Professional Coders, the 90-day global period accounts for approximately 70% of major surgical procedure codes in the CPT manual.
The global surgical package encompasses a range of services included in the global period, as per CMS guidelines. This includes:
Excluded are unrelated treatments, diagnostic tests, or returns to the OR for complications.
For Your Information:
Practices must now report all postoperative visits using CPT code 99024 (Postoperative follow-up visit, normally included in the surgical package). While this code carries $0 reimbursement, CMS mandates reporting in select states to collect data for future valuation adjustments.
Medicare global period rules are widely used as the industry standard that many private insurers follow. CMS guidelines outline the surgical billing and documentation requirements for the global surgical package.
For 90-day global surgical procedures, surgeons must use Modifier -54 (Surgical Care Only) when they perform only the surgery and do not provide postoperative care, even if there is no formal transfer of care.
CMS introduced HCPCS code G0559 to allow separate payment for postoperative follow-up care provided by a different practitioner when the original surgeon does not provide that care and no formal transfer was documented.
CMS is working to improve payment accuracy by encouraging the correct use of global surgery modifiers and reviewing claims data.
CPT code 99024 may be reported by some practices to track postoperative follow-up visits that are normally included in the global surgical package. Reporting CPT 99024 is used for data collection and payment accuracy and is not required nationwide by CMS for all states or specialties.
Billing during the global period requires precision. Use modifiers for global period billing to unbundle unrelated services:
For E/M billing during the global period, append modifiers only for distinct services.
Hello MDs supports this through medical coding services, ensuring modifiers are applied accurately to avoid errors.
Errors in global period billing are common and can result in lost revenue:
HelloMDs’ denial management specialists utilize automated rules engines that catch these errors before submission, reducing global period-related denials by 68% for their clients.
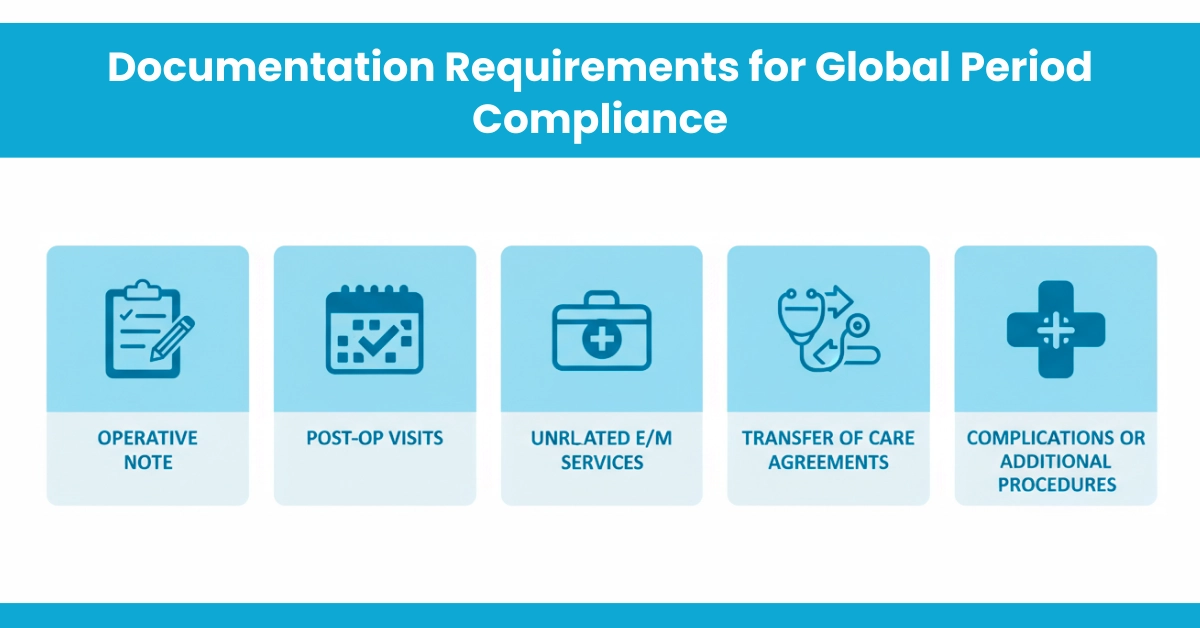
Operative Note: Clearly document the procedure, date, and any planned follow-up care.
Post-Op Visits: Record all post-op encounters, including who provided care and any complications.
Unrelated E/M Services: Document the reason for any evaluation during the global period and use the appropriate modifier (e.g., Modifier 24).
Transfer of Care Agreements: Keep written agreements if a PA/NP or other provider manages post-op care.
Complications or Additional Procedures: Document fully, including diagnoses, interventions, and dates.
Achieve global period compliance with these steps:
In 2026, prioritise HCPCS G0559 for non-surgical postoperative care. Hello MDs aids compliance via physician billing services, minimizing risks in specialities like therapy.
Mastering the global period in medical billing is key to accurate reimbursement and practice compliance. Understanding which services are included in the surgical package, correctly applying modifiers, and maintaining thorough documentation prevent costly denials and audits. With CMS 2025-26 updates such as HCPCS G0559 and stricter reporting requirements, staying current is more important than ever. Proper global period management ensures providers are fully compensated for their work while reducing revenue cycle risks. Partnering with HelloMDs helps practices navigate complex billing rules efficiently, minimize errors, and focus on delivering high-quality patient care without financial disruptions.
Disclaimer:
This content is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended as medical billing, coding, legal, or compliance advice. For Proper Guidance, contact the Hello Mds team. Some visuals used in this blog are AI-generated and included only to help illustrate concepts clearly.
It is a defined timeframe covering preoperative, operative, and postoperative services bundled into a single reimbursement.
Unrelated procedures, complications requiring return to the operating room, and separately identifiable evaluation services may be billed.
CPT procedures usually carry zero-day, ten-day, or ninety-day global periods, determining postoperative billing restrictions.
Modifier 24 is used to report unrelated evaluation and management services during the postoperative global period.
The global period generally applies per surgeon or group, allowing other providers to bill independently for unrelated care.