Home / Long-Term Use of Insulin ICD-10
If your practice manages diabetic patients, you’re probably familiar with the routine: document the diabetes, code the diabetes, submit the claim. You’ve probably typed Z79.4 more times than you can count in your whole service. But do you ever pause and wonder if you’re using it correctly every single time or not? One tiny oversight, and the claim comes bouncing faster than you can say “denial,” and denials.
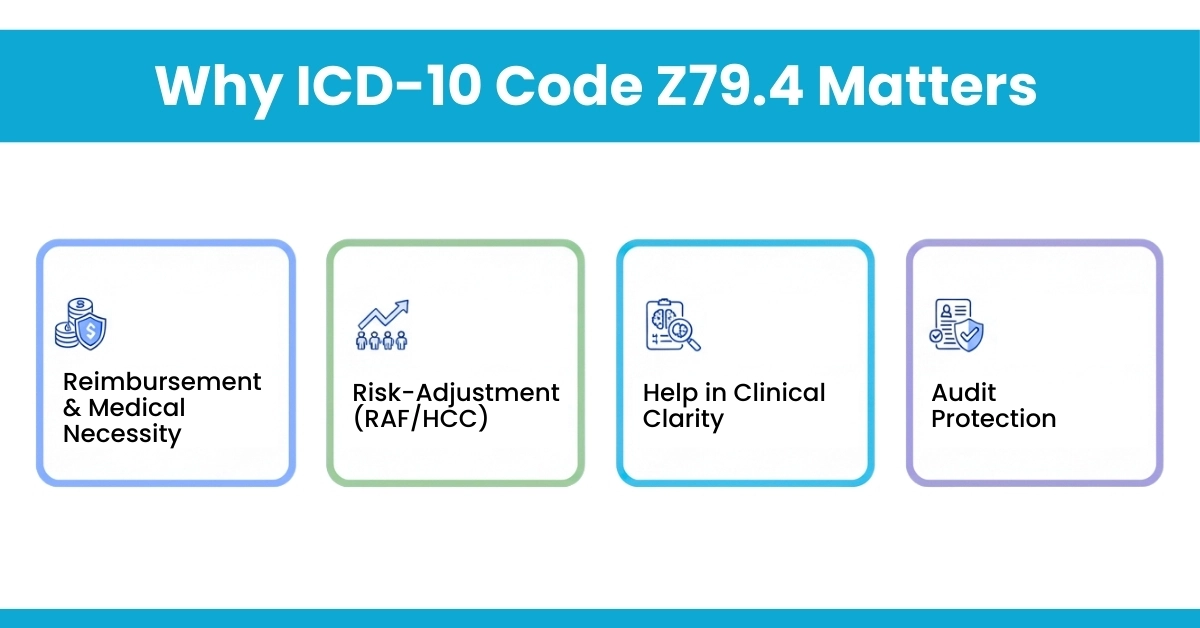
Accurate coding for long-term use of insulin ICD-10 isn’t just about compliance. It directly impacts your reimbursement, risk-adjustment (HCC/RAF), and even patient access to medication. This guide will show you exactly how to capture every valid dollar while staying compliant.
The official code is Z79.4 – Long-term (current) use of insulin. It is part of the Z79 family of codes.
Here’s what makes ICD-10 z79.4 unique:
Expert Biller Tip: There were no changes to Z79.4 itself. However, the expansion of Z79.85 has made coders accidentally shift insulin-dependent patients to the wrong Z code. Don’t let that happen to you.
Properly documenting long-term insulin use helps support claims for DME (pumps, infusion supplies, CGMs), many payers require that you show that insulin isn’t just being used short-term.
In value-based care (like Medicare Advantage), documenting Z79.4 can contribute to HCC or RAF scoring, influencing payments and patient risk profiles.
Using Z79.4 tells a more complete story: not just that a patient has diabetes, but that they are on chronic insulin therapy, which may affect care planning, lab monitoring, and patient education.
Detailed, guideline-aligned documentation reduces audit risk. When Z79.4 is properly supported, payers and auditors are less likely to challenge the claim.
For your information:
A 2024 analysis of medical billing audit services data showed that practices using automated Z code capture saw a 4.3% increase in collected revenue per diabetic patient.
Source: ASCO Daily News
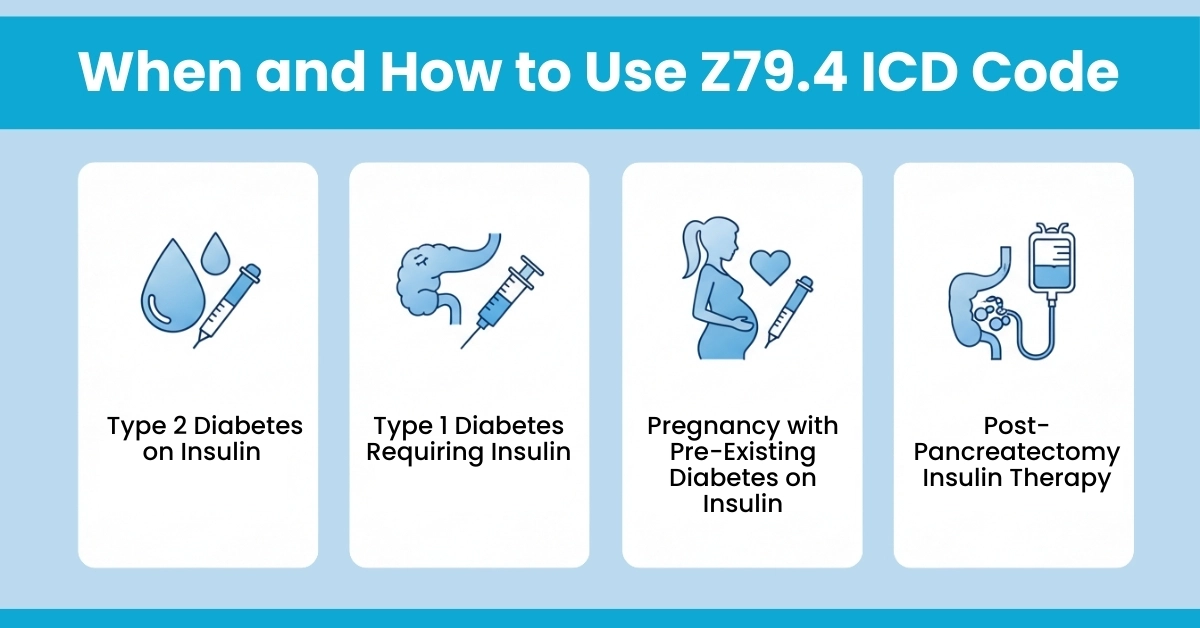
Here are common clinical scenarios and how to apply Z79.4 correctly, per ICD-10-CM guidelines.
The Patient: 58-year-old with Type 2 diabetes, using Lantus 20 units nightly plus metformin. A1c is 7.2%.
Why: This reflects both the diabetes diagnosis and the therapeutic regimen of insulin and oral medicine.
Common Error: Coding only E11.9. This misses the insulin therapy ICD-10 code and underreports complexity.
The Patient: 25-year-old with Type 1 diabetes on an insulin pump.
Critical Note: Even though Type 1 implies insulin use, Z79.4 is still appropriate under current ICD-10-CM guidelines when documentation supports ongoing insulin use. The FY 2024/FY 2025 ICD-10-CM guidelines no longer clearly exclude Z79.4 for E10.x (Type 1 diabetes), so many coders now include it for clarity, especially when the provider notes long-term insulin use. This specificity helps ensure your coding accurately reflects the patient’s insulin therapy plan.
The Patient: 32-year-old, 16 weeks pregnant, with pre-existing Type 2 diabetes managed on insulin.
The Patient: Post-Whipple (after surgical removal of the pancreas), the patient now has diabetes requiring insulin.
Why: This combination captures the cause of diabetes (post-surgical), the diabetes type, and the long-term therapy status.
According to the ICD-10-CM guidelines, do not assign Z79.4 in these situations:
All of these qualify for Z79.4 when used long-term:
Category | Examples |
Rapid-acting | Humalog, NovoLog, Fiasp, Lyumjev, Admelog, Apidra |
Short-acting | Humulin R, Novolin R |
Intermediate | Humulin N, Novolin N |
Long-acting | Lantus, Levemir, Tresiba, Toujeo, Basaglar, Semglee |
Ultra-long | Ryzodeg, Xultophy (combo) |
Premixed | Humalog Mix 75/25, NovoLog Mix 70/30 |
Insulin pump/CSII | Any brand used continuously |
There is NO separate code for glargine ICD-10 or Lantus ICD-10—everything routes to Z79.4.
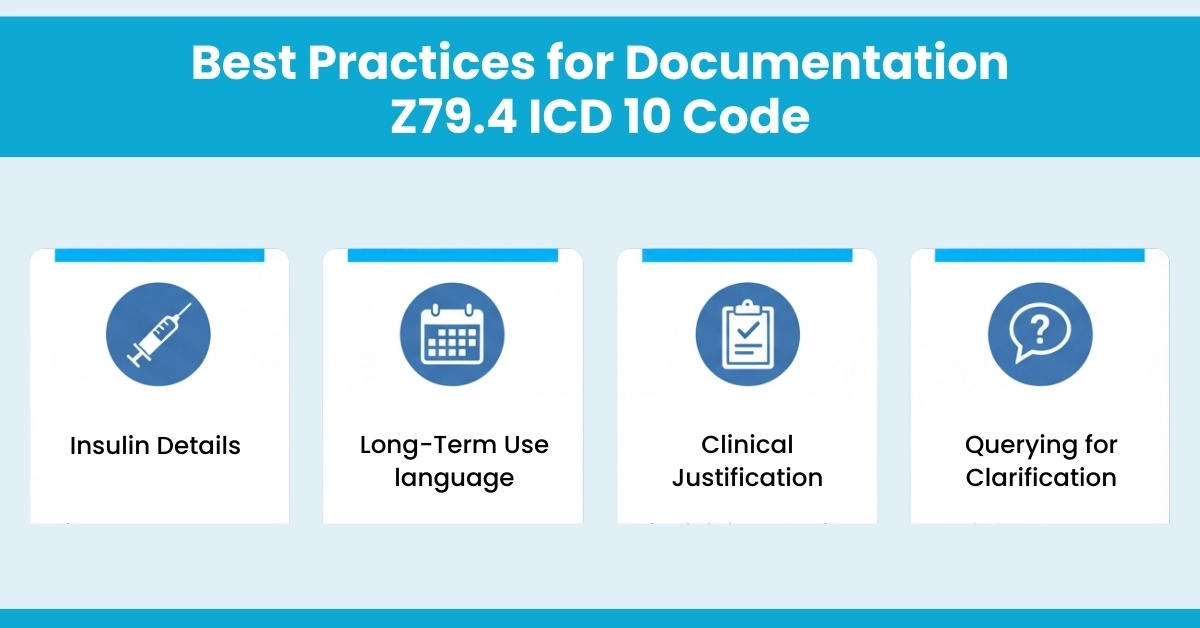
To minimize denials and support audits, ensure your documentation meets the following:
Note: Z79.4 – long-term use of Insulin helps healthcare providers accurately document and manage ongoing insulin therapy. Understanding proper ICD-10 coding ensures streamlined claims and compliance, similar to how ICD-10 Obesity and Its Codes are applied for chronic conditions like obesity.
Our denial management team sees these errors weekly. Avoid them:
Our Hello MDs medical billing services include monthly Z code audits, catching Z79.4 gaps before external auditors do. This proactive approach reduced client audit liabilities by 38%.
The long-term use of insulin ICD-10 coding isn’t about memorizing guidelines—it’s about recognizing that ICD-10 compliance for insulin use is directly tied to your practice’s financial health. Every missing Z79.4 is a small crack in your revenue foundation.
Practices that perform quarterly Z79.4 audits capture an average of $127 more per insulin-dependent Medicare Advantage patient annually. That’s money already earned; you just need to code for it.
At HelloMDS, we don’t treat coding as paperwork. We treat it as revenue intelligence. Our physician billing services, integrated payment posting, and proactive denial management ensure that when your patient uses insulin, your insurance billing for insulin therapy captures every legitimate dollar.
Disclaimer:
This guide provides general information about ICD-10 coding for insulin therapy. For billing guidance specific to your practice, consult our certified medical billing specialist at Hello MDs. Some images in this content are AI-made and only for illustration
The ICD-10 code for long-term insulin use is Z79.4. This code indicates that a patient is currently using insulin as part of their ongoing diabetes management.
Z79.4 is for long-term use of insulin, while Z79.84 is for long-term use of oral hypoglycemic drugs. Patients on both can have both codes on the same claim.
Yes, Z79.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used for reimbursement purposes as either a primary or secondary diagnosis.
Documentation should include the insulin type, dosage, frequency, route of administration, and indication that it's part of the patient's long-term treatment plan.
According to ICD-10-CM guidelines: