If you’re a busy pulmonologist, medical coder, or practice manager dealing with respiratory cases, let’s talk straight about the ICD-10 code for bronchitis. It is an important thing not just for clinical accuracy, but for avoiding claim denials and ensuring proper reimbursement.
At Hello MDs, we’ve seen how inaccurate coding can delay payments or trigger audits. With years of experience in pulmonary RCM, our AAPC-certified coders have helped practices reduce bronchitis-related denials.
In this guide, we will break down ICD-10 codes for acute and chronic bronchitis, documentation tips, pitfalls, and even 2025 updates, all based on official CMS and AAPC standards. Plus, we’ll show how our team supports your claims process every step of the way.
Bronchitis is the swelling and irritation of the bronchial tubes, the airways responsible for transporting air to and from the lungs. It typically leads to cough, mucus production, and breathing issues.
The ICD-10-CM code for bronchitis standardizes this for billing, reporting and reimbursement. As the ICD code 10 for bronchitis, it ensures compliance with HIPAA and payer rules.
At Hello MDs, our certified medical coders specialize in ICD-10 coding for respiratory diseases. By ensuring accurate and specific documentation, we help pulmonary providers reduce claim denials, improve compliance, and protect revenue integrity.
For sudden-onset cases, start with the ICD-10 code for acute bronchitis—J20.9 for unspecified. This is your default when no pathogen is identified, per ICD-10 guidelines Section I.C.10.a.
Need more detail?
From AAPC resources, always classify based on acute vs chronic classification. Here’s a trusted breakdown:
Code | Description | Guidelines (CMS/AAPC) |
J20.4 | Acute bronchitis due to parainfluenza virus | Use if parainfluenza is confirmed via labs or provider documentation. Consider adding Z87.891 (history of tobacco) if applicable. |
J20.6 | Acute bronchitis due to rhinovirus | Common in seasonal outbreaks. May be coded with asthma if both are documented as separate conditions. |
J20.7 | Acute bronchitis due to echovirus | Rare; use when echovirus is confirmed. Document onset to support sequencing in complex cases. |
Here are commonly used subcodes (and when they apply):
Code | Description | When to Use / Notes |
J20.0 | Acute bronchitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae | Use only with physician documentation or lab confirmation |
J20.1 | Acute bronchitis due to Haemophilus influenzae | Use only with strong clinical or lab evidence |
J20.2 | Acute bronchitis due to Streptococcus | Confirmed bacterial etiology required |
J20.3 | Acute bronchitis due to Coxsackievirus | Use when viral cause confirmed |
J20.4 | Acute bronchitis due to parainfluenza virus | Confirmed via lab testing or provider diagnosis |
J20.5 | Acute bronchitis due to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) | Valid 2025 billable code |
J20.6 | Acute bronchitis due to rhinovirus | Common in seasonal outbreaks, valid for 2025 |
J20.7 | Acute bronchitis due to echovirus | Rare; use only if documented |
J20.8 | Acute bronchitis due to other specified organisms | For identified organisms not listed elsewhere |
J20.9 | Acute bronchitis, unspecified | Default when no specific pathogen identified |
Key Tip: If documentation does not support a more specific pathogen, do not upcode. The unspecified subtype (J20.9) is the defensible choice.
Chronic bronchitis requires a cough for 3 months in 2 years (WHO criteria). The mainstay ICD-10 code for chronic bronchitis is J42 unspecified.
Comorbid scenarios demand care:
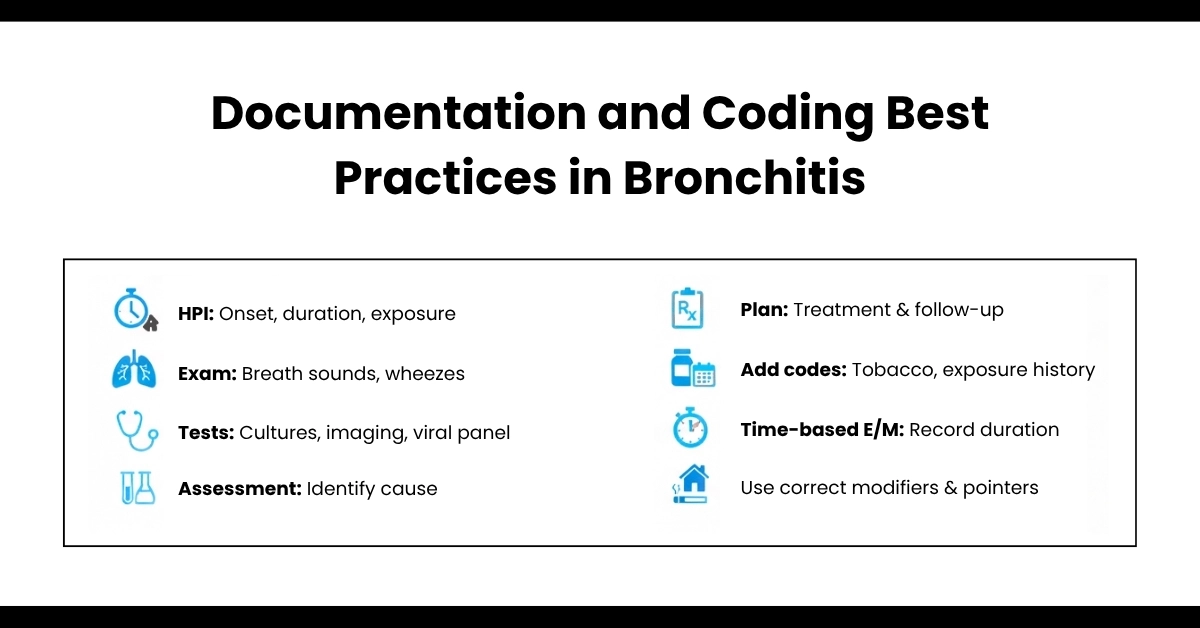
Trustworthy Tip: Note diagnosis certainty (confirmed via spirometry) and onset date. CDC updates emphasize excluding codes like J40 unless acuity is truly unknown; it’s often denied for lack of specificity.
Note: Since bronchitis often leads to increased white blood cell counts, you can also explore our article on ICD-10 Leukocytosis to understand how such findings affect billing accuracy.
At Hello MDs we ensure this via expert reviews, aligning with medical billing for respiratory diseases.
Although this guide is diagnosis-focused, you will often pair with procedure/treatment codes:
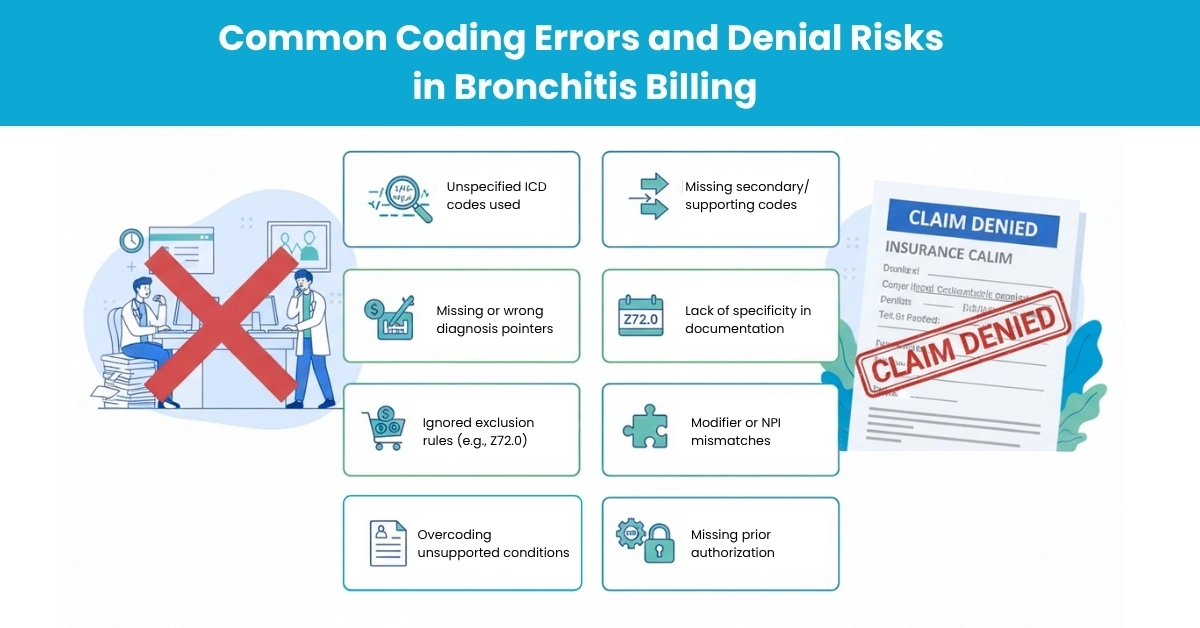
From audits and industry reports, frequent mistakes include:
Hello MDs’ denial management team leverages this knowledge to recover funds and appeal effectively.
We’ve helped clients steadily improve clean claim rates in respiratory service lines, and we back our services with defensible, guideline-aligned practices.
Accurate ICD-10 coding for acute and chronic bronchitis is essential to ensure proper billing, compliance, and to prevent costly claim denials. Staying updated with the latest 2025 coding guidelines and best practices helps providers navigate complex cases, especially when bronchitis overlaps with conditions like COPD or asthma. Proper documentation and code selection not only protect revenue but also support quality patient care.
At Hello MDs, our expert AAPC-certified coders and billing specialists are dedicated to helping practices achieve coding accuracy and streamline their revenue cycle, so you can focus on what matters most—your patients.
Disclaimer:
For informational purposes only; not intended as medical or billing advice. Always verify codes with official ICD-10 guidelines or call Hello Mds’ coding professionals. Some visuals may be AI-created for demonstration purposes.
Use J20.9 for unspecified acute bronchitis when no pathogen is identified or documented.
Report J44.9 (COPD unspecified) as the primary diagnosis, with J42 (chronic bronchitis) as secondary if applicable.
Specific pathogen codes (e.g., J20.0-J20.7) require provider documentation or lab confirmation. Otherwise, use unspecified J20.9 to avoid upcoding risks.
No major bronchitis-specific changes in 2025, but FY 2026 updates will bring refinements, especially for COPD and chemical inhalation codes.