Home / Medicare 8 Minute Rule for Physical Therapy
The 8 minute rule is a Medicare guideline used to determine how to bill for timed therapy services (physical, occupational, and speech therapy). The services are billed based on time spent performing therapeutic activities, not just sessions or appointments. And this applies only when the therapy is timed, i.e., codes where time dictates billing.

Following is a 8-minute rule table for easy coding:
Therapy Type | CPT Code | Timed? | Time Range (Minutes) | Units | Modifier | Notes / CMS Guidance |
Physical Therapy | 97110 – Therapeutic Exercise | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GP | Exercises, strengthening, range of motion |
Physical Therapy | 97110 | Yes | 23–37 | 2 | GP | 2 units = add 15 min total |
Physical Therapy | 97110 | Yes | 38–52 | 3 | GP | Add units per 15 min increments |
Physical Therapy | 97112 – Neuromuscular Re-education | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GP | Includes balance, coordination |
Physical Therapy | 97116 – Gait Training | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GP | Each 15 min increment = 1 unit |
Physical Therapy | 97530 – Therapeutic Activities | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GP | Functional activities, timed |
Occupational Therapy | 97165 – Evaluation (Low Complexity) | No | N/A | 1 per session | GO | Not timed, one per session |
Occupational Therapy | 97535 – Self-Care/Home Management | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GO | ADL or functional activity |
Occupational Therapy | 97110 – Therapeutic Exercise | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GO | Same PT code can be OT if functional |
Speech Therapy | 92507 – Treatment of Speech/Language | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GN | Timed speech-language therapy |
Speech Therapy | 92523 – Eval of Speech/Language | No | N/A | 1 per session | GN | Non-timed evaluation |
Speech Therapy | 92526 – Treatment of Swallowing | Yes | 8–22 | 1 | GN | Swallowing/feeding therapy, timed |
Please note that providers are suggested not to bill in case only 1 service is provided in a day, and that too was performed in less than 8 minutes. Here is how you may calculate:
Round down to the nearest unit if under 8 minutes.
For step-wise assistance, you may find it useful to check out the CMS regulations and guidance manual.
Note: While the 8-Minute Rule defines how therapy minutes are billed under Medicare, insurance providers such as UnitedHealthcare also require prior authorization for therapy services. Learn more about UnitedHealthcare’s new prior authorization rules here.
Following these notes may help you avoid expensive denials:
Want to offload your administrative load?
Get a no-obligation quotation from HelloMDs, a HIPAA-compliant medical billing service.
Implementation of the 8-minute rule made easy:
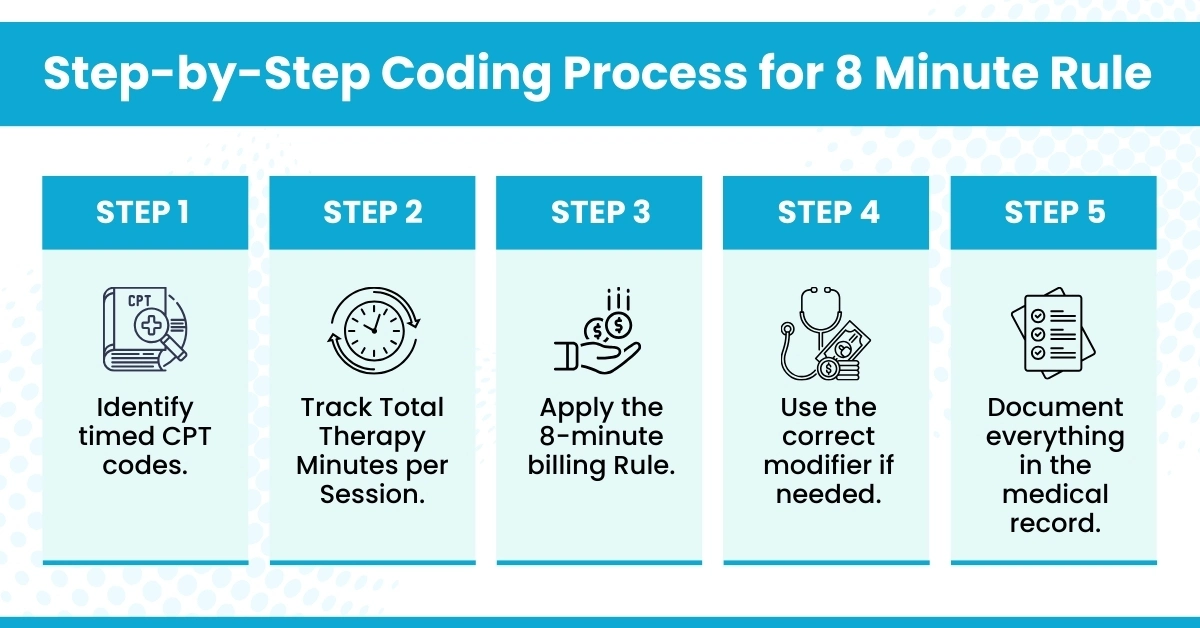
The Medicare 8-minute rule physical therapy ensures accurate, compliant billing for timed therapy sessions. Track time meticulously, code correctly, and you’ll maximize reimbursement while staying fully compliant. Or simply consider offloading your administrative tasks to a HIPAA-compliant medical billing company like Hello MDs.
Disclaimer: This blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical, legal, or professional advice. While we strive for accuracy, errors or omissions may occur.